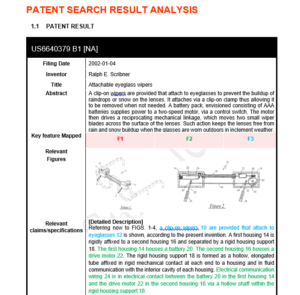
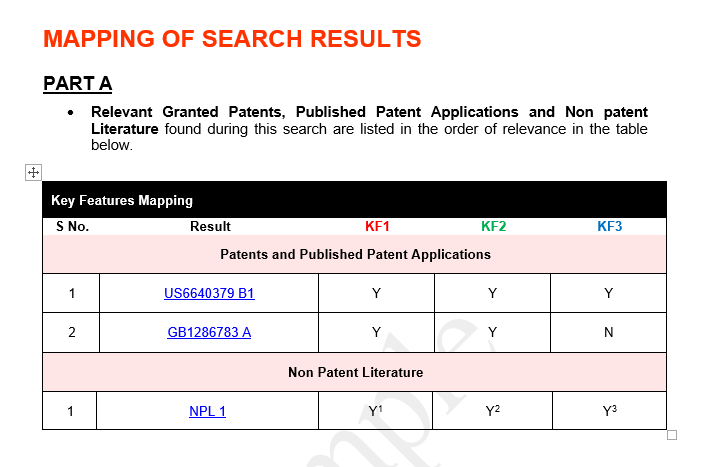
Patent Search
Patentability Search
A Patentability Search / Novelty search / Prior Art Search is performed to evaluate the patentability of an invention. This should help to estimate the chances of success of the application, i.e. the chances of obtaining a patent.
Invalidity Search
A Patent Invalidation search is performed to invalidate or revoke an already registered / granted patent claims or for a pre-grant opposition of a published patent application claims. It involves identifying prior art references including patent references and non patent literature.
Freedom to Operate Search
A Freedom To Operate (FTO)/clearance search is performed to assess the risk of potential infringement. Freedom to Operate (FTO) refers to whether it’s commercially ‘safe’ for you to make or sell your product in the country in which you wish to do so, without infringing existing third-party rights.
Design Search
A design patent search is the process of identifying existing patents to determine if a new design is unique and non-infringing. This search typically involves using the International Design Classification (LOC) or the U.S. Patent Classification (USPC) systems to categorize designs based on their visual characteristics.
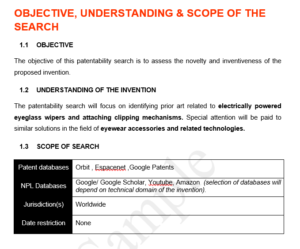
Patentability / Novelty Search
- Definition: A patentability search is an examination to assess whether an invention meets the requirements for obtaining a patent.
- Purpose: Determines if the invention is novel (new) and non-obvious compared to existing technologies.
- Process: Conducted by searching patent databases and other sources for prior art (existing patents, publications, etc.) related to the invention.
- Criteria: Evaluates the invention against patentability standards: novelty (not previously disclosed) and non-obviousness (an unexpected advancement).
- Outcome: Provides insights into the likelihood of successfully obtaining a patent and informs strategic decisions in the patenting process.

Invalidity / Validity Search
- Obtain Patent Information: Gather the patent number and details about the target claims of subject patent.
- File Wrapper Analysis for Novelty identification: Reviewing the prosecution history (file wrapper) of the patent and examines the correspondence between the applicant and the patent office during examination.
- Search for Prior Art: Look for previous patents, scientific papers, or other publications that disclose similar inventions before the earliest priority date.
- Analyze Claims: Focus on the specific features of the patent's claims and compare them to the prior art.
- Identify Anticipation or Obviousness: Find references that might show the invention lacks novelty (anticipation) or is obvious.
- Compile Evidence: Gather relevant prior art to demonstrate why the patent may be invalid.

Freedom To Operate/ Clearance Search
- Objective: To identify any patents that might pose a risk of infringement.
- Scope: Searches typically cover patents in relevant jurisdictions where the product or process is intended to be used or sold.
- Focus: Identifying existing patents and pending applications that could overlap with the proposed product or technology. The search targets active patent claims that could cover the technology or product in question.
- Assessment: Evaluates the scope of these claims and compares them with the intended product or process to determine potential infringement risks.
- Outcome: Helps ensure that the product or process can be developed, sold, or used without violating the patent rights of others.


Design Search
- Locating design patents: This search focuses specifically on design patents, which protect the visual aspects or ornamental features of a product (e.g., shape, pattern, surface ornamentation), as opposed to its functionality. Evaluating uniqueness: Determining if the design you're interested in is novel and non-obvious compared to existing designs.
- Classify Designs: Use Locarno Classification or other design-specific codes.
- Image Search: Utilize image-based search tools when available.
- Check Legal Status: Confirm if patents are active, expired, or pending
